684. Redundant Connection
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
Example 1:
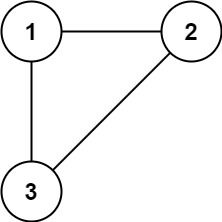
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]] Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
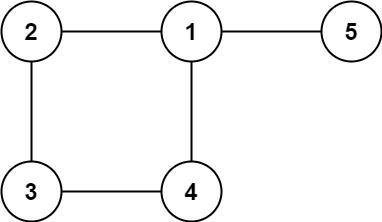
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]] Output: [1,4]
Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- The given graph is connected.
JAVA
class Solution { private int[] p; public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) { p = new int[1010]; for (int i = 0; i < p.length; ++i) { p[i] = i; } for (int[] e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (find(a) == find(b)) { return e; } p[find(a)] = find(b); } return null; } private int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } }
C++
class Solution { public: vector<int> p; vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) { p.resize(1010); for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) p[i] = i; for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (find(a) == find(b)) return e; p[find(a)] = find(b); } return {}; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } };
PYTHON
class Solution: def findRedundantConnection(self, edges): p = list(range(1010)) def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) # Path compression return p[x] for a, b in edges: if find(a) == find(b): return [a, b] p[find(a)] = find(b) return None
Comments
Post a Comment