2493. Divide Nodes Into the Maximum Number of Groups
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes in an undirected graph. The nodes are labeled from 1 to n.
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is a bidirectional edge between nodes ai and bi. Notice that the given graph may be disconnected.
Divide the nodes of the graph into m groups (1-indexed) such that:
Each node in the graph belongs to exactly one group.
For every pair of nodes in the graph that are connected by an edge
[ai, bi], ifaibelongs to the group with indexx, andbibelongs to the group with indexy, then|y - x| = 1.
Return the maximum number of groups (i.e., maximum **m) into which you can divide the nodes. Return -1 **if it is impossible to group the nodes with the given conditions.
Example 1:
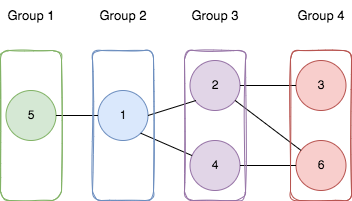
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,3],[4,6]]
Output: 4
Explanation: As shown in the image we:
- Add node 5 to the first group.
- Add node 1 to the second group.
- Add nodes 2 and 4 to the third group.
- Add nodes 3 and 6 to the fourth group.
We can see that every edge is satisfied.
It can be shown that that if we create a fifth group and move any node from the third or fourth group to it, at least on of the edges will not be satisfied.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: If we add node 1 to the first group, node 2 to the second group, and node 3 to the third group to satisfy the first two edges, we can see that the third edge will not be satisfied.
It can be shown that no grouping is possible.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != biThere is at most one edge between any pair of vertices.
JAVA
class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
private boolean[] vis;
private int n;
public int magnificentSets(int n, int[][] edges) {
g = new List[n + 1];
this.n = n;
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
vis = new boolean[n + 1];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!vis[i]) {
dfs(i);
int t = -1;
for (int v : arr) {
t = Math.max(t, bfs(v));
}
if (t == -1) {
return -1;
}
ans += t;
arr.clear();
}
}
return ans;
}
private int bfs(int k) {
int[] dist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, 1 << 30);
dist[k] = 1;
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(k);
int ans = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int i = q.pollFirst();
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (dist[j] == 1 << 30) {
dist[j] = dist[i] + 1;
ans = dist[j];
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
for (int i : arr) {
if (dist[i] == 1 << 30) {
dist[i] = ++ans;
}
}
for (int i : arr) {
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (Math.abs(dist[i] - dist[j]) != 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
arr.add(i);
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
}
}C++
class Solution { public: int magnificentSets(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<vector<int>> g(n + 1); for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].emplace_back(b); g[b].emplace_back(a); } vector<int> arr; bool vis[n + 1]; memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis); int ans = 0; function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) { arr.emplace_back(i); vis[i] = true; for (int& j : g[i]) { if (!vis[j]) { dfs(j); } } }; auto bfs = [&](int k) { int ans = 1; int dist[n + 1]; memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); dist[k] = 1; queue<int> q{ {k} }; while (!q.empty()) { int i = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int& j : g[i]) { if (dist[j] == 0x3f3f3f3f) { ans = dist[j] = dist[i] + 1; q.push(j); } } } for (int& i : arr) { if (dist[i] == 0x3f3f3f3f) { dist[i] = ++ans; } } for (int& i : arr) { for (int& j : g[i]) { if (abs(dist[i] - dist[j]) != 1) { return -1; } } } return ans; }; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (!vis[i]) { dfs(i); int t = -1; for (int& v : arr) t = max(t, bfs(v)); if (t == -1) return -1; ans += t; arr.clear(); } } return ans; } };
PYTHON
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def magnificentSets(self, n, edges):
g = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
# Build the graph
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
vis = [False] * (n + 1)
ans = 0
def dfs(i):
arr.append(i)
vis[i] = True
for j in g[i]:
if not vis[j]:
dfs(j)
def bfs(k):
dist = [float('inf')] * (n + 1)
dist[k] = 1
q = deque([k])
max_depth = 1
while q:
i = q.popleft()
for j in g[i]:
if dist[j] == float('inf'):
dist[j] = dist[i] + 1
max_depth = dist[j]
q.append(j)
for i in arr:
if dist[i] == float('inf'):
return -1
for i in arr:
for j in g[i]:
if abs(dist[i] - dist[j]) != 1:
return -1
return max_depth
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if not vis[i]:
arr = []
dfs(i)
max_depth = max(bfs(v) for v in arr)
if max_depth == -1:
return -1
ans += max_depth
return ans
Comments
Post a Comment