3243 - Shortest Distance After Road Addition Queries I
You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array queries.
There are n cities numbered from 0 to n - 1. Initially, there is a unidirectional road from city i to city i + 1 for all 0 <= i < n - 1.
queries[i] = [ui, vi] represents the addition of a new unidirectional road from city ui to city vi. After each query, you need to find the length of the shortest path from city 0 to city n - 1.
Return an array answer where for each i in the range [0, queries.length - 1], answer[i] is the length of the shortest path from city 0 to city n - 1 after processing the first i + 1 queries.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, queries = [[2,4],[0,2],[0,4]]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:
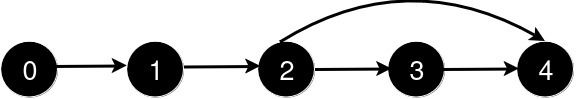
After the addition of the road from 2 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 3.
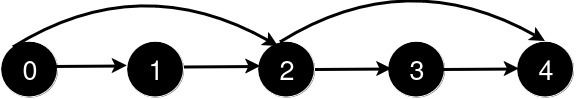
After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 2.
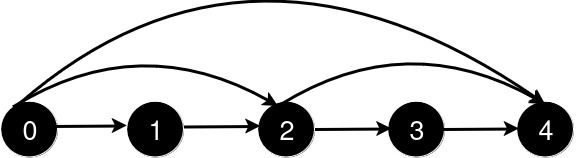
After the addition of the road from 0 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, queries = [[0,3],[0,2]]
Output: [1,1]
Explanation:
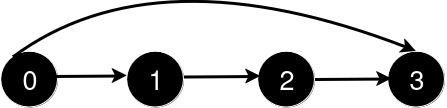
After the addition of the road from 0 to 3, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 3 is 1.
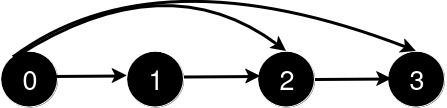
After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path remains 1.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 5001 <= queries.length <= 500queries[i].length == 20 <= queries[i][0] < queries[i][1] < n1 < queries[i][1] - queries[i][0]- There are no repeated roads among the queries.
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> shortestDistanceAfterQueries(int n, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
vector<int> g[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
g[i].push_back(i + 1);
}
auto bfs = [&](int i) -> int {
queue<int> q{ {i} };
vector<bool> vis(n);
vis[i] = true;
for (int d = 0;; ++d) {
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
if (u == n - 1) {
return d;
}
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
};
vector<int> ans;
for (const auto& q : queries) {
g[q[0]].push_back(q[1]);
ans.push_back(bfs(0));
}
return ans;
}
};PYTHON
from collections import deque class Solution: def shortestDistanceAfterQueries(self, n, queries): g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for i in range(n - 1): g[i].append(i + 1) def bfs(i): q = deque([i]) vis = [False] * n vis[i] = True d = 0 while q: for _ in range(len(q)): u = q.popleft() if u == n - 1: return d for v in g[u]: if not vis[v]: vis[v] = True q.append(v) d += 1 ans = [] for q in queries: g[q[0]].append(q[1]) ans.append(bfs(0)) return ans
class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private int n; public int[] shortestDistanceAfterQueries(int n, int[][] queries) { this.n = n; g = new List[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) { g[i].add(i + 1); } int m = queries.length; int[] ans = new int[m]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { int u = queries[i][0], v = queries[i][1]; g[u].add(v); ans[i] = bfs(0); } return ans; } private int bfs(int i) { Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(i); boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; vis[i] = true; for (int d = 0;; ++d) { for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) { int u = q.poll(); if (u == n - 1) { return d; } for (int v : g[u]) { if (!vis[v]) { vis[v] = true; q.offer(v); } } } } } }
Comments
Post a Comment